Amortization Schedule For Bonds Issued At Face Value

Bonds issued at face value on an interest date valley company s accounting year ends on december 31.
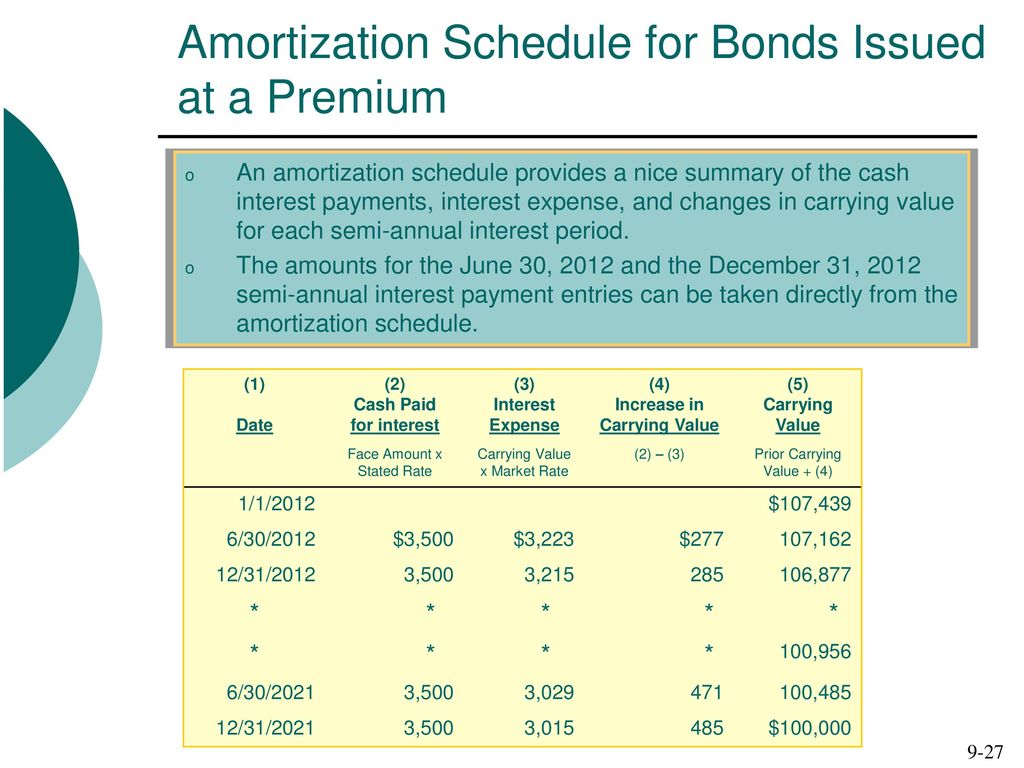
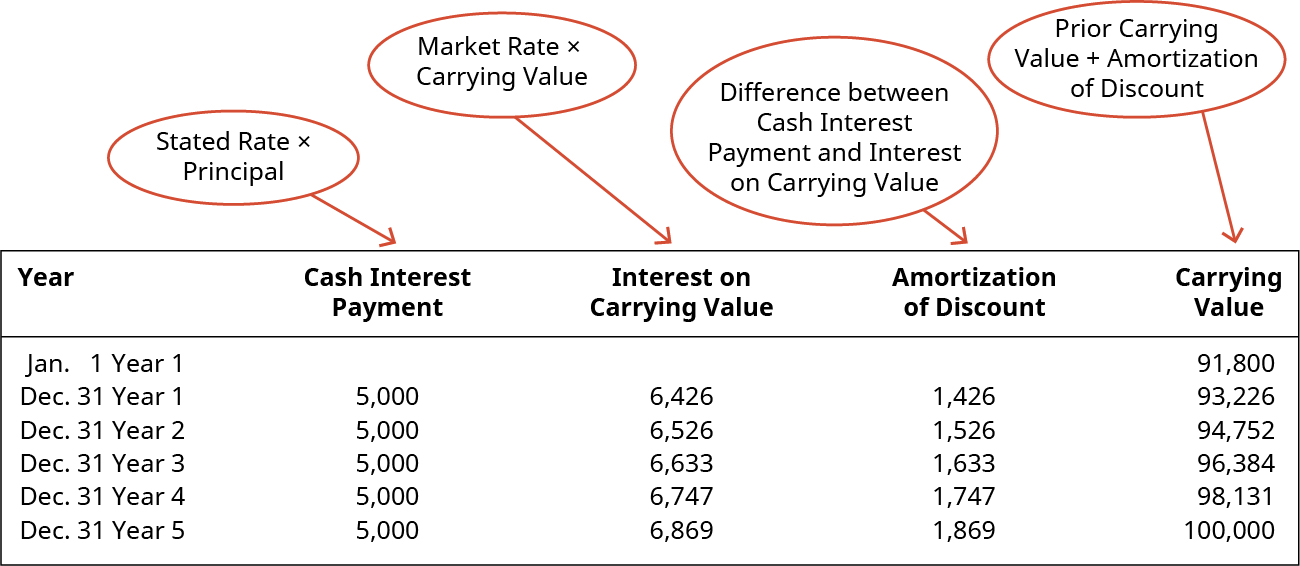
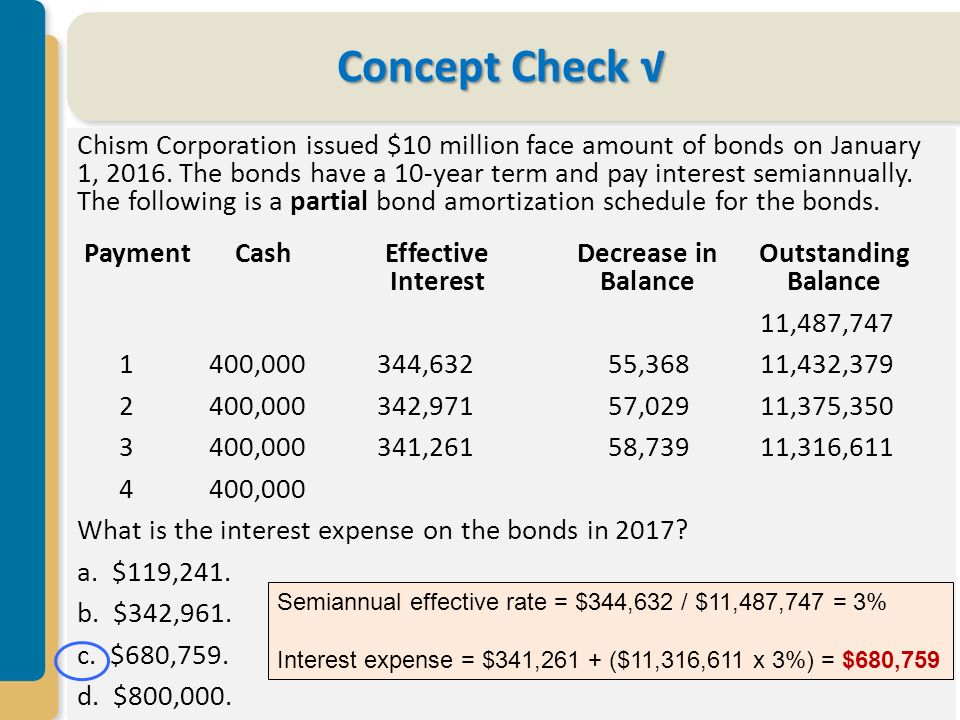
Amortization schedule for bonds issued at face value. The carrying value of a bond refers to the net amount between the bond s face value plus any un amortized premiums or minus any amortized discounts. Bond discount with straight line amortization. An amortization schedule is used to compute the percentage that is interest and the percentage that is principal within each bond payment. The corporation must make an interest payment of 4 500 100 000 x 9 x 6 12 on each june 30 and december 31.
The bond amortization calculator calculates the bond issue price which is a function of both the bond rate and the market rate. Fill the cash paid column with one half the coupon rate times the bond face value. Two accounting methods are used for amortizing bond. An amortization schedule lists each interest payment and reconciles it with interest expense showing period wise amortization of bond premium.
The carrying value is also commonly referred. For example if the four year bond has a face value of 1 000 and pays a 7 percent coupon set cash paid rows 2. Enter the annual market interest rate at the date the bond is issued. This interest expense is then compared to the actual interest payment based on the face value of the bond and the bond rate and the difference gives the amount to be amortized to the interest expense account.
In other words amortization is an accounting technique to adjust bond premium over the life of the bond. On 2010 december 31 valley issued 10 year 12 per cent bonds with a 100 000 face value for. It is useful to create an amortization schedule in such a situation. Let s assume that the corporation prepares a 100 000 bond with an interest rate of 9.
The issuer has to amortize the bond premium over the life of the bond which in turn reduces the amount charged to interest expense. The effective interest method involves preparing a bond amortization schedule to calculate the interest expense based on the market rate at the time the bond was issued and the bonds book value. Enter the par value of the bonds issued. When a corporation is preparing a bond to be issued sold to investors it may have to anticipate the interest rate to appear on the face of the bond and in its legal contract.
The following examples illustrate the accounting for bonds issued at face value on an interest date and issued at face value between interest dates.



/abstract-mirror-building-texture-1027237872-b97473a76afd421f886da92f046bc9fb.jpg)
/GettyImages-1086691530-8ca9071cc0a2461fa175ba845bd29e83.jpg)
/GettyImages-1005470094-ebdbd294840149df97c833b856a567e1.jpg)
/sell-house-941800424-567f763277c9421398c308ce5bc40376.jpg)

/GettyImages-1027438182-64a291df9eaf4bcda87cd8f9fdd6bc8a.jpg)

